In industrial, automotive, and electronic applications, protecting cables, wires, and hoses is critical to maintaining system reliability and safety. One of the most effective and versatile solutions for this purpose is spiral wrap. Whether you are working with hydraulic lines, electrical wiring, or pneumatic hoses, knowing how to apply a spiral wrap correctly can significantly extend the lifespan of your components while improving overall organization and safety.
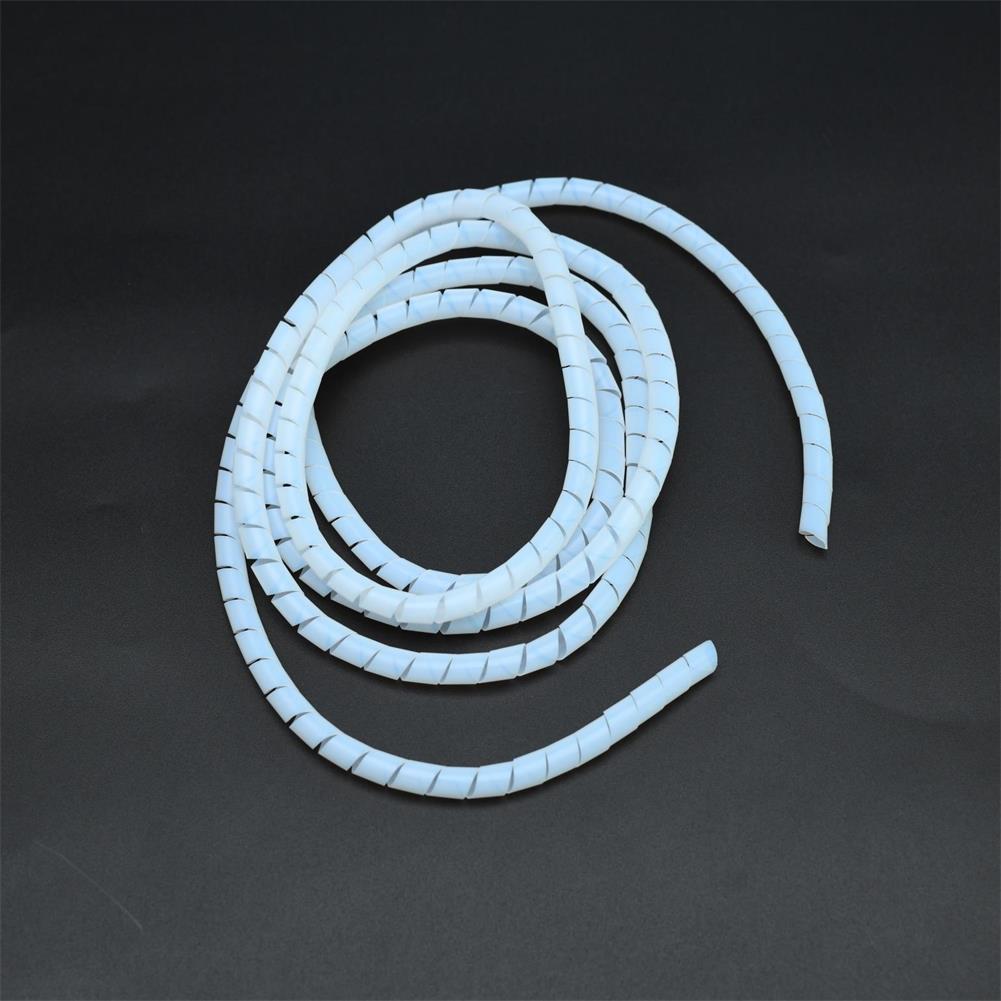

This guide explores everything you need to know about Spiral Wrap Tubing, spiral wire wrap, spiral hose wrap, heli tube spiral wrap, PTFE Spiral Wrap, and spiral hose protectors, including material selection, installation methods, and practical tips for maximizing durability.
What Is Spiral Wrap?
Spiral wrap is a flexible, helical sheath designed to encase wires, cables, or hoses. It protects against abrasion, chafing, heat, moisture, and mechanical stress while keeping multiple lines neatly bundled.
Common types include:
Spiral wrap tubing: Typically made from polyethylene, nylon, or PTFE, used for wire and hose protection.
Spiral wire wrap: Specifically designed for electrical wiring, providing flexibility and easy installation.
Spiral hose wrap: Protects hydraulic or pneumatic hoses from wear and external damage.
Heli tube spiral wrap: A spiral wrap variant for specialized tubing applications, often used in aerospace and automotive industries.
PTFE spiral wrap: Offers exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, ideal for harsh industrial environments.
Spiral hose protector: Reinforces hoses in high-abrasion or high-stress applications.
By understanding these types, you can select the right spiral wrap for your application before moving on to proper installation techniques.
Why Use Spiral Wrap?
Using a spiral wrap provides several advantages:
Protection Against Abrasion and Mechanical Damage: Cables and hoses moving over surfaces or rubbing against each other are vulnerable to wear. A spiral hose protector mitigates this risk.
Organization and Safety: A clean, bundled system reduces tangling, prevents accidental tripping, and makes maintenance easier.
Heat and Chemical Resistance: Materials such as PTFE allow spiral wrap tubing to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive chemicals.
Flexibility and Expandability: Unlike rigid conduits, spiral wraps allow expansion and movement while maintaining protection.
Cost-Effective Maintenance: Protecting hoses and wires reduces downtime and replacement costs.
How Should a Spiral Wrap Be Applied?
Applying spiral wrap may seem straightforward, but proper technique ensures maximum protection and longevity. Follow these steps:
1. Measure the Cable or Hose Length
Begin by measuring the total length of the cable, hose, or bundle you want to protect. This ensures you purchase the correct amount of spiral wire wrap or spiral hose wrap.
2. Select the Right Spiral Wrap
Choose the wrap based on diameter, material, and application:
Spiral wrap tubing: Best for general-purpose wiring and hose bundling.
PTFE spiral wrap: Ideal for high-temperature, chemical-resistant applications.
Heli tube spiral wrap: Designed for specialized aerospace or automotive tubing.
The inner diameter of the wrap should be slightly larger than the largest cable or hose in the bundle to allow easy installation while maintaining snug protection.
3. Start Wrapping from One End
Begin at one end of the cable or hose. Insert the first few centimeters of the bundle into the center of the spiral wrap. Slowly rotate the wrap around the cable in a helical motion.
For spiral wire wrap, maintain a tight, even spiral.
For spiral hose wrap, ensure the wrap covers the entire surface, leaving minimal gaps.
4. Maintain Proper Tension
Do not stretch the spiral wrap tubing excessively, as over-tension can deform the material or reduce its protective properties. Keep consistent tension to achieve uniform coverage.
5. Continue Wrapping Along the Entire Length
Advance the wrap along the cable or hose in a smooth motion. For longer bundles, it may be helpful to have one person hold the cable while another wraps.
6. Secure the Ends
Once the wrap reaches the opposite end, you can secure it using:
Cable ties
Heat-shrink tubing (for electrical wires)
End caps or clips (for hoses)
Proper end fastening prevents the wrap from unraveling during operation.
Tips for Installing Spiral Wrap Effectively
Avoid sharp bends: Excessive bending can stress the wrap and underlying wires or hoses.
Overlap slightly at joints: If wrapping multiple sections, a small overlap ensures continuous protection.
Use appropriate tools: Spiral wrap installation tools or mandrels make wrapping faster and reduce manual strain.
Consider expansion: Choose a spiral wrap with enough flexibility to accommodate movement or thermal expansion of hoses.
Mark critical sections: For maintenance, marking wrapped sections can help identify high-wear or inspection points.
Applications of Spiral Wrap
Industrial Machinery
In factories, cables and hydraulic hoses are frequently exposed to friction and mechanical stress. A spiral hose protector can prevent abrasion, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the life of hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Automotive Industry
Wiring harnesses and fluid lines in vehicles are protected with spiral wire wrap or spiral hose wrap. The flexibility of the wrap allows components to move freely while preventing chafing and wear.
Aerospace and Aviation
Heli tube spiral wrap is widely used in aerospace applications to protect sensitive tubing and wiring. PTFE or high-performance materials ensure resistance to chemicals, high temperatures, and vibration.
Electronics and Electrical Systems
In electrical panels and electronic assemblies, spiral wrap tubing organizes wires neatly, prevents tangling, and reduces electrical interference. It also facilitates inspection and maintenance without disconnecting the entire system.
Advantages of PTFE Spiral Wrap
A PTFE spiral wrap is a high-performance option for extreme environments:
Excellent chemical and corrosion resistance
High-temperature tolerance
Non-stick and self-lubricating surface
Long service life under harsh operating conditions
PTFE wraps are ideal for chemical plants, laboratories, aerospace, and high-performance automotive applications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Choosing the wrong diameter: Too small causes tight tension, too large reduces protection.
Skipping securing steps: Unsecured ends can unravel quickly.
Overstretching the wrap: Deforms the material and reduces durability.
Ignoring movement and expansion: Wrapping too tightly in dynamic applications can lead to premature wear.
Using the wrong material: Choose PTFE for chemical resistance or standard polyethylene for general-purpose protection.
Maintenance and Inspection
Even the best spiral wrap tubing requires periodic inspection:
Check for fraying or cuts
Ensure the ends are still secured
Replace sections showing excessive wear
For dynamic hoses, verify that the wrap is not restricting movement
Routine maintenance maximizes the lifespan of both the wrap and the protected cables or hoses.
Conclusion
A spiral wrap is an essential tool for protecting wires, hoses, and tubes across multiple industries. From standard spiral wire wrap and spiral hose wrap to high-performance PTFE spiral wrap and heli tube spiral wrap, selecting the right type and applying it correctly ensures safety, durability, and efficiency.
By following proper installation steps—including selecting the correct size, maintaining tension, wrapping evenly, and securing the ends—you can maximize the effectiveness of your spiral hose protector or spiral wrap tubing. Whether for industrial machinery, automotive systems, aerospace components, or electronic wiring, spiral wraps remain a cost-effective and reliable solution for cable and hose management.