When choosing tubing materials for industrial, medical, laboratory, or electronics applications, many engineers ask: Is PTFE tubing flexible? The answer is yes, but its flexibility depends on several factors—diameter, wall thickness, temperature, and the specific application. To fully understand this, we must first look at what PTFE tubing is, how it behaves mechanically, and how it compares to other materials such as Kynar plastic and Silicone Heat Shrink tubing.
This article offers an in-depth explanation of PTFE tubing flexibility, performance features, applications, and how it compares to similar products.
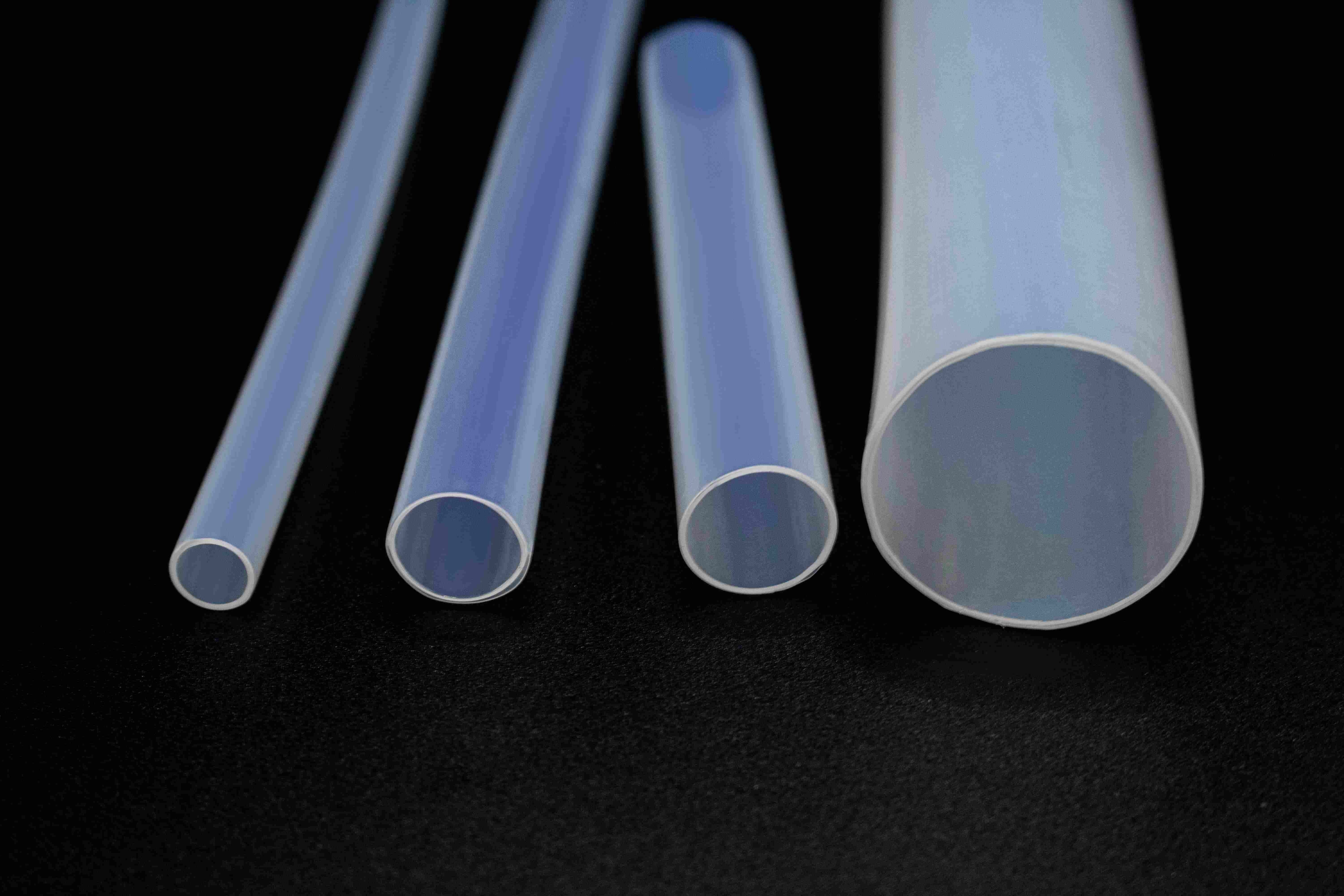
What Is PTFE Tubing?
Before discussing flexibility, let’s clarify: What is PTFE tubing?
PTFE, also known by its brand name Teflon, is a fluoropolymer with exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction. PTFE tubing (or Teflon tubing) is a hollow tube extruded from pure PTFE resin. It is widely used in environments requiring:
High temperatures
Harsh chemical exposure
Electrical insulation
Extremely smooth internal surfaces
Non-reactive and non-stick characteristics
Because PTFE is so chemically inert, it is also a common material used for PTFE gasket production.
Is PTFE Tubing Flexible? The Short Answer
Yes — PTFE tubing is flexible, but not in the same way as silicone or rubber.
PTFE is a semi-rigid fluoropolymer, meaning:
It bends, but does not stretch.
It is flexible, but not “soft.”
Thinner-wall PTFE tubing offers more pliability.
Larger-size PTFE tubes are stiffer due to geometry.
In most industrial applications, PTFE tubing is considered moderately flexible, capable of bending without breaking but maintaining its shape.
What Determines PTFE Tubing Flexibility?
Several factors affect how flexible or rigid PTFE tubing feels:
1. Wall Thickness
Thin-wall PTFE tubing → more flexible, easy to route around corners.
Thick-wall PTFE tubing → more rigid, better for high-pressure applications.
2. Tube Diameter
Smaller inner diameters are generally easier to bend. Larger tubes require more force and may maintain a straight shape unless heated.
3. Temperature
PTFE becomes softer and more flexible when heated. Flexibility improves significantly above:
80–100°C for general bending
150°C+ for tight-radius bends
This is why PTFE is often thermoformed for custom shapes.
4. Manufacturing Process
Some PTFE tubes are made from paste extrusion (more flexible), while others are made using ram extrusion (slightly more rigid).
Why PTFE Tubing Is Still Considered Flexible
Compared with metals or rigid plastics, PTFE tubing offers several flexibility advantages:
It can bend without cracking.
It tolerates repeated bending cycles better than brittle plastics.
It retains flexibility across a wide temperature range (−200°C to +260°C).
This makes PTFE tubing, Teflon tubing, and various PTFE gasket components preferred for dynamic, high-performance systems.
How Flexible Is PTFE Tubing Compared to Other Materials?
To better understand PTFE flexibility, let’s compare it with several commonly used tubing materials.
PTFE Tubing vs. Kynar Plastic (PVDF Tubing)
Kynar plastic (PVDF) is another high-performance fluoropolymer but offers greater rigidity than PTFE.
| Property | PTFE Tubing | Kynar Plastic (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Moderate | Lower (more rigid) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Very good |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260°C | Up to 150°C |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Conclusion:
If maximum chemical and thermal resistance are needed, PTFE tubing is the better choice. If a slightly rigid structure is desired, Kynar plastic is ideal.
PTFE Tubing vs. Silicone Heat Shrink Tubing
Silicone heat shrink tubing has a completely different type of flexibility. Silicone is:
Soft
Elastic
Stretchable
Compressible
In comparison:
| Property | PTFE Tubing | Silicone Heat Shrink Tubing |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Semi-rigid | Very soft and flexible |
| Elasticity | Non-elastic | Highly elastic |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Heat Shrink | No | Yes |
Conclusion:
If you need soft, rubber-like flexibility, silicone heat shrink tubing is best. If the application demands chemical resistance and high temperatures, PTFE tubing is the superior choice.
Why PTFE Tubing Is Used Even If It’s Not Extremely Soft
Even though PTFE tubing is not as flexible as silicone or rubber, engineers still select it because:
1. It withstands extreme temperatures
PTFE remains stable from -200°C to 260°C, which very few materials can match.
2. It is chemically inert
PTFE tubing resists nearly all acids, solvents, fuels, and corrosive chemicals.
3. It has the lowest friction coefficient of any solid
This allows smooth fluid or gas flow with minimal pressure drop.
4. It provides excellent electrical insulation
Common in high-voltage, RF, and aerospace applications.
5. It is non-stick and low absorption
Fluids flow cleanly, making it ideal for pharmaceutical and laboratory environments.
6. It handles UV and weather exposure well
PTFE does not degrade outdoors.
Where PTFE Tubing Flexibility Matters Most
Though semi-rigid, PTFE tubing is used in many flexible-routing systems such as:
1. Chemical Transfer Lines
Its inertness allows safe transport of acids, solvents, and reactive fluids.
2. Medical Equipment
Flexible PTFE tubing is used for catheter liners, surgical tools, and lab analysis.
3. Electrical Insulation
PTFE tubing provides bendable yet durable insulation for wiring in:
Aerospace
Automotive
Electronics
Telecommunications
4. Semiconductor Manufacturing
PTFE tolerates aggressive etching chemicals while routing easily in tight spaces.
5. Food and Beverage Processing
Its non-stick properties prevent contamination and buildup.
6. 3D Printers and CNC Machines
PTFE tubes guide filament or air lines with smooth low-friction pathways.
How to Make PTFE Tubing More Flexible
If your application requires additional flexibility, you can modify PTFE tubing performance by:
1. Choosing thin-wall designs
These bend more easily without losing durability.
2. Increasing temperature
Heating PTFE to around 100–150°C makes it bend easily for shaping.
3. Using corrugated PTFE tubing
This increases flexibility dramatically for vacuum or robotics applications.
4. Selecting smaller diameters
Narrow tubes bend more naturally.
Applications Where PTFE Flexibility Is Critical
1. Robotic Arms
PTFE tubing routes air or chemicals with minimal friction.
2. Analytical Instruments
Precise, smooth fluid flow is essential.
3. High-Temperature Furnaces
Flexible routing helps avoid sharp bends that may crack other tubing types.
4. Automotive Fuel Lines
PTFE withstands ethanol, gasoline, and high heat.
5. Pharmaceutical Transfer
Flexible PTFE ensures contamination-free fluid movement.
Is PTFE Tubing the Right Choice for Your Project?
You should choose PTFE tubing or Teflon tubing if your application requires:
Exceptional chemical resistance
High temperature endurance
Smooth, low-friction fluid movement
Nonstick interior
Durable yet moderately flexible routing
If you need soft, elastic flexibility, then silicone heat shrink tubing is more suitable.
If you want a rigid, chemical-resistant structure, Kynar plastic may be better.
Conclusion: PTFE Tubing Is Flexible — But With Limits
So, is PTFE tubing flexible?
Yes, PTFE tubing offers moderate flexibility, especially in thin-wall and small-diameter formats. While not as soft as silicone, it provides a unique combination of:
Flexibility
Strength
Chemical resistance
Temperature stability
Nonstick performance
This balance makes PTFE tubing, Teflon tubing, and PTFE gasket components essential across industries—from aerospace to medical, from chemical processing to electronics.